
High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) Symptoms, Causes and more
High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure (hypertension) is a common situation wherein the long-term pressure of the blood in opposition to your artery walls is high enough that it could ultimately cause health problems, such as heart disease.
Hypertension takes place when the force of blood pushing thru your vessels is constantly too high. In this article, we’ll cover the fundamentals of hypertension (high blood pressure), along with its signs and symptoms, causes, the way it’s treated, and more.
Hypertension is quite commonplace. In fact, the reason that guidelines changed in 2017, is that almost half of American adults ought to now be diagnosed with this condition.
Lose Weight Naturally / 10 Ways To Lose Weight Naturally
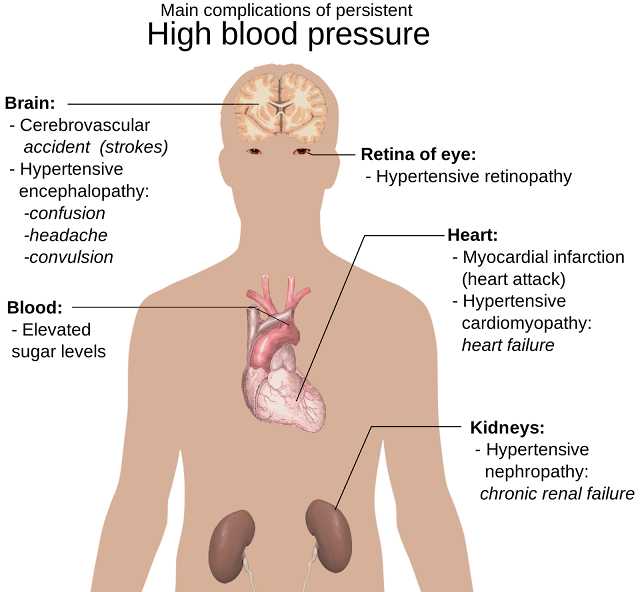
High blood pressure generally develops over the course of numerous years. normally, you don’t observe any symptoms. However, even without signs and symptoms, high blood pressure can cause harm to your blood vessels and organs, especially the brain, coronary heart, eyes, and kidneys.
Treatment for high blood pressure (hypertension) includes both prescription medicine and healthful lifestyle changes. If the situation isn’t handled, it can cause health problems, such as heart attack and stroke.
Two numbers create a blood pressure reading.
Systolic pressure (top number) shows the pressure in your arteries whilst your heart beats and pumps out blood.
Diastolic pressure (bottom number) is the reading of the pressure in your arteries between beats of your coronary heart.
What are the symptoms of high blood pressure?
Many individuals are unsure that they have high blood pressure (hypertension) because there are no warning signs or symptoms. The only method to inform whether you have high blood pressure is to check your blood pressure.
Hypertension is commonly a silent condition. Many humans won’t experience any signs and symptoms. It could take years or maybe a long time for the condition to attain levels severe enough that symptoms emerge as obvious.
A few people with high blood pressure might also have headaches, shortness of breath, or nosebleeds. However, these signs and symptoms are not precise and generally do not arise until high blood pressure (hypertension) has reached a severe or life-threatening stage.
What is the cause of high blood pressure?
There are two types of high blood pressure. Every type has a distinctive cause.
Primary (essential) hypertension
For most adults, there may be no identifiable cause of high blood pressure. This type of high blood pressure, called primary (essential) hypertension (high blood pressure), has a tendency to increase step by step over many years.
A mixture of factors generally play a role in the development of primary (essential) high blood pressure (hypertension):
- Age
- Genes
- High alcohol consumption
- living with weight problems
- Race
- Living with diabetes and/or metabolic syndrome
Secondary hypertension
A few human beings have high blood pressure or hypertension caused by an underlying situation. This type of high blood pressure, known as secondary hypertension, has a tendency to appear suddenly and cause higher blood pressure than primary high blood pressure. Numerous conditions and medications can cause secondary high blood pressure, including:
- Kidney disease
- Thyroid problems
- Aspect outcomes of medicinal drugs
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Congenital in blood vessels
- Use of illegal drugs, which include cocaine and amphetamines

Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) (Joint Pain) Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Causes
Diagnosis of high blood pressure
Your physician will do a bodily examination and ask you questions about your medical history. A medical doctor, nurse, or a different clinical assistant will place an inflatable arm cuff over your arm and use a pressure-measuring gauge to take your blood pressure.
Whether there is a change in your blood pressure, you should check it in both arms. It’s vital to utilize an arm cuff that’s the appropriate size.
The importance of both values in a blood pressure measurement cannot be overstated. However, around the age of 50, the systolic measurement becomes even more critical. Isolated systolic hypertension is characterized by a normal diastolic pressure (less than 80 mm Hg) but a high systolic pressure (greater than or equal to 130 mm Hg). This is a kind of high blood pressure that is frequent in people over the age of 65.
Because blood pressure changes throughout the day and might increase during a visit to the doctor (white coat hypertension). Your doctor will most likely take multiple blood pressure measurements across three or more appointments prior to diagnosing you with high blood pressure.
Check Blood Pressure at Home Self-Measured Blood Pressure (SMBP):
Speak with your doctor about checking your blood pressure at home on a regular basis, commonly known as self-measured blood pressure (SMBP) monitoring.
Home monitoring is a vital tool for confirming whether or not you have high blood pressure, assessing whether or not your blood pressure treatment is working, and diagnosing worsening high blood pressure.
Tests
Whether you have high blood pressure, your doctor may advise tests to confirm the diagnosis and rule out whatever underlying conditions that can cause hypertension.
- Ambulatory monitoring
- Lab tests
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)
- Echocardiogram
High Blood Pressure Treatment
Many individuals with hypertension may reduce their blood pressure or keep their readings in a safe range by changing their lifestyles. Consult your healthcare team about it.
- Lowering sodium (salt) and alcohol intake as part of a healthy diet
- Each week, engage in at least 150 minutes of physical activity (about 30 minutes a day, 5 days a week)Smoking cessation
- Maintaining a healthy body weight
- Stress management

If you noticed you have high blood pressure or have been informed you have high blood pressure but it is not under control, contact your healthcare professional immediately once.
However, lifestyle adjustments are not always sufficient. Whenever exercise and diet don’t work, your doctor may prescribe blood pressure medication.
Medications
The type of medicine prescribed by your doctor for high blood pressure is decided on your blood pressure readings and overall health. Two or more blood pressure medicines are frequently more effective than one. Finding the best effective medicine or drug combination is sometimes a matter of trial and error.
Inquire with your doctor about the best blood pressure treatment plan for you. Furthermore, the appropriate blood pressure treatment objective varies with age and health conditions, especially if you are over the age of 65.
Among the medications wont to treat high vital signs are:
- Diuretics: chlorthalidone, hydrochlorothiazide (Microzide) and others.
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors: lisinopril (Prinivil, Zestril), benazepril (Lotensin), captopril, and others.
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs): candesartan (Atacand), losartan (Cozaar) and others.
- Calcium channel blockers: amlodipine (Norvasc), diltiazem (Cardizem, Tiazac, others), and others.
High blood pressure can sometimes be treated with additional drugs:
- Alpha blockers: doxazosin (Cardura), prazosin (Minipress) and others.
- Alpha-beta blockers: carvedilol (Coreg) and labetalol (Trandate) and others.
- Beta blockers: acebutolol, atenolol (Tenormin), and others.
- Aldosterone antagonists: spironolactone and eplerenone (Inspra) and others.
- Renin inhibitors: Aliskiren (Tekturna) and others.
- Vasodilators: hydralazine and minoxidil and others.
- Central-acting agents: clonidine (Catapres, Kapvay), guanfacine (Intuniv), methyldopa, and others.
Conclusion
High blood pressure is not something that can be treated and then ignored. It’s a condition you’ll have to deal with for the rest of your life. To keep your blood pressure checked.
It is never too early to start making healthy lifestyle changes like stopping smoking, eating healthier foods, and exercising more. These are the most effective techniques to prevent high blood pressure and associated consequences, such as heart attack and stroke.